CentOS course notes
networking
Network Manager CLI: nmcli
list all interfaces:
ip a
centos
example: /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3
naming:
en: Ethernet Network
p0: bus PCI n°0
s3: slot 3
@ip detail fro interface enp0s3
ip addr show enp0s3
Create a virtualbox nat network: 10.0.3.0/24
10.0.3.1: gateway
10.0.3.2: gateway
10.0.3.3: DNS
1st @ip is: 10.0.3.4
static @ip
vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3
TYPE="Ethernet"
NM_CONTROLLED="no"
PROXY_METHOD="none"
BROWSER_ONLY="no"
BOOTPROTO="static"
DEFROUTE="yes"
IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL="no"
IPV6INIT="no"
#IPV6_AUTOCONF="yes"
#IPV6_DEFROUTE="yes"
#IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL="no"
#IPV6_ADDR_GEN_MODE="stable-privacy"
IPADDR=10.0.3.5
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
GATEWAY=10.0.3.1
DNS1=1.1.1.1
NAME="enp0s3"
UUID="f7b6b794-8d98-4c80-93ed-1b2ce803457e"
DEVICE="enp0s3"
ONBOOT="yes"
systemctl restart network
ping 1.1.1.1
ping google.fr
show internal route table: ip route
default via 10.0.3.1 dev enp0s3
10.0.3.0/24 dev enp0s3 proto kernel scope link src 10.0.3.5
169.254.0.0/16 dev enp0s3 scope link metric 1002
ARP Adress resolution Protocol : mapping @mac <=>@IP
ip n show
Firewall
firewall-cmd --get-default-zone
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service https
firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-all
public (active)
target: default
icmp-block-inversion: no
interfaces: enp0s3
sources:
services: dhcpv6-client https ssh
ports:
protocols:
masquerade: no
forward-ports:
source-ports:
icmp-blocks:
rich rules:
Virtualbox guest additions
click 'insert guest addition CD'
mount /dev/cdrom /media/cdrom
cd /media/cdrom
KERN_DIR=/usr/src/kernels/$(uname -r)
export KERN_DIR
./VBoxLinuxAdditions.run
MATE GUI
yum install -y epel-release
yum groupinstall -y "MATE Desktop"
systemctl set-default graphical.target
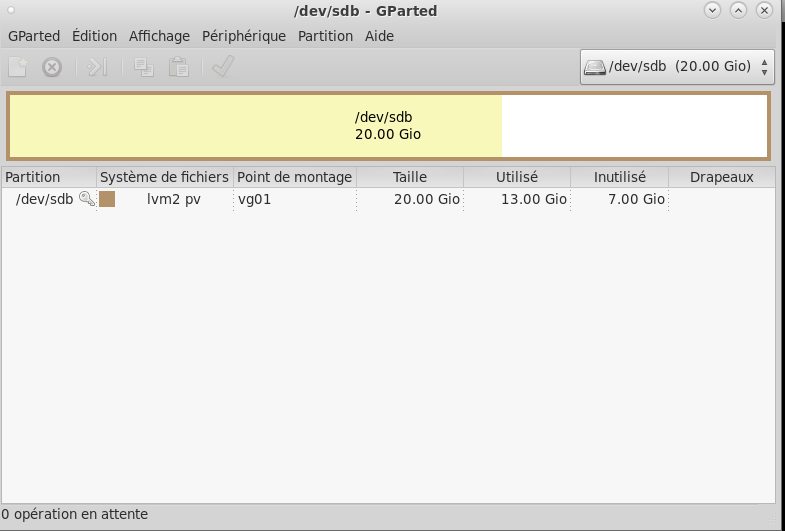
Partitioning
Create a physical partition
fdisk /dev/sdb
Bienvenue dans fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2).
Les modifications resteront en mémoire jusqu'à écriture.
Soyez prudent avant d'utiliser la commande d'écriture.
Le périphérique ne contient pas de table de partitions reconnue
Construction d'une nouvelle étiquette pour disque de type DOS avec identifiant de disque 0xf858f73b.
Commande (m pour l'aide) : m
Commande d'action
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition
g create a new empty GPT partition table
G create an IRIX (SGI) partition table
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition's system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only)
Commande (m pour l'aide) : n
Type de partition :
p primaire (0 primaire(s), 0 étendue(s), 4 libre(s))
e étendue
Sélection (p par défaut) : p
Numéro de partition (1-4, 1 par défaut) : 1
Premier secteur (2048-41943039, 2048 par défaut) :
Utilisation de la valeur 2048 par défaut
Dernier secteur, +secteur ou +taille{K,M,G} (2048-41943039, 41943039 par défaut) : +5G
La partition 1 de type Linux et de taille 5 GiB est configurée
Commande (m pour l'aide) : m
Commande d'action
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition
g create a new empty GPT partition table
G create an IRIX (SGI) partition table
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition's system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only)
Commande (m pour l'aide) : w
La table de partitions a été altérée.
Appel d'ioctl() pour relire la table de partitions.
Synchronisation des disques.
partition créé, non formatée; inutilisable pour le moment
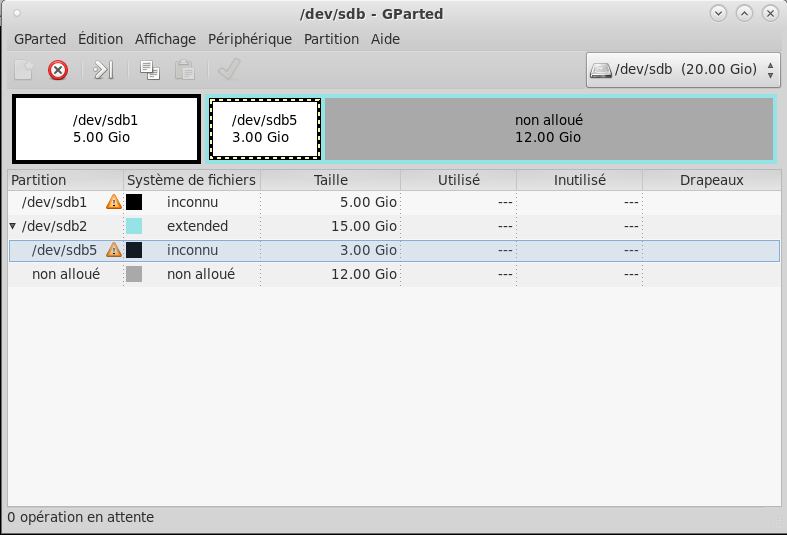
Create a 15 GO extended partition on all remaning space
fdisk /dev/sdb
Bienvenue dans fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2).
Les modifications resteront en mémoire jusqu'à écriture.
Soyez prudent avant d'utiliser la commande d'écriture.
Commande (m pour l'aide) : n
Type de partition :
p primaire (1 primaire(s), 0 étendue(s), 3 libre(s))
e étendue
Sélection (p par défaut) : e
Numéro de partition (2-4, 2 par défaut) : 2
Premier secteur (10487808-41943039, 10487808 par défaut) :
Utilisation de la valeur 10487808 par défaut
Dernier secteur, +secteur ou +taille{K,M,G} (10487808-41943039, 41943039 par défaut) :
Utilisation de la valeur 41943039 par défaut
La partition 2 de type Extended et de taille 15 GiB est configurée
Add 3Go logical partition inside the extended partition
Commande (m pour l'aide) : n
Type de partition :
p primaire (1 primaire(s), 1 étendue(s), 2 libre(s))
l logique (numéroté à partir de 5)
Sélection (p par défaut) : l
Ajout de la partition logique 5
Premier secteur (10489856-41943039, 10489856 par défaut) :
Utilisation de la valeur 10489856 par défaut
Dernier secteur, +secteur ou +taille{K,M,G} (10489856-41943039, 41943039 par défaut) : +3G
La partition 5 de type Linux et de taille 3 GiB est configurée
Commande (m pour l'aide) : p
Disque /dev/sdb : 21.5 Go, 21474836480 octets, 41943040 secteurs
Unités = secteur de 1 × 512 = 512 octets
Taille de secteur (logique / physique) : 512 octets / 512 octets
taille d'E/S (minimale / optimale) : 512 octets / 512 octets
Type d'étiquette de disque : dos
Identifiant de disque : 0xf858f73b
Périphérique Amorçage Début Fin Blocs Id. Système
/dev/sdb1 2048 10487807 5242880 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 10487808 41943039 15727616 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 10489856 16781311 3145728 83 Linux
Commande (m pour l'aide) : w
La table de partitions a été altérée.
Appel d'ioctl() pour relire la table de partitions.
Synchronisation des disques.
LVM
Declare physical volumes
[root@centos ~]# pvcreate /dev/sdb
WARNING: dos signature detected on /dev/sdb at offset 510. Wipe it? [y/n]: y
Wiping dos signature on /dev/sdb.
Physical volume "/dev/sdb" successfully created.
[root@centos ~]# pvcreate /dev/sdc
Physical volume "/dev/sdc" successfully created.
[root@centos ~]# vgcreate vg01 /dev/sd
sda sda1 sda2 sdb sdc
Create a volume group: vg01
[root@centos ~]# vgcreate vg01 /dev/sdb /dev/sdc
Volume group "vg01" successfully created
[root@centos ~]# vgdisplay vg01
--- Volume group ---
VG Name vg01
System ID
Format lvm2
Metadata Areas 2
Metadata Sequence No 1
VG Access read/write
VG Status resizable
MAX LV 0
Cur LV 0
Open LV 0
Max PV 0
Cur PV 2
Act PV 2
VG Size 39,99 GiB
PE Size 4,00 MiB
Total PE 10238
Alloc PE / Size 0 / 0
Free PE / Size 10238 / 39,99 GiB
VG UUID LoVhMG-uCtl-jw9H-LjCv-k5zh-jjoO-50w0S7
Create logical volumes
[root@centos ~]# lvcreate -n lv01 -L 5Go /dev/vg01
Logical volume "lv01" created.
[root@centos ~]# lvcreate -n lv02 -L 15Go /dev/vg01
Logical volume "lv02" created.
[root@centos ~]# lvcreate -n lv03 -L 8Go /dev/vg01
Logical volume "lv03" created.
Ext4 formating of logical volumes
root@centos ~]# mkfs -t ext4 /dev/vg01/lv01
mke2fs 1.42.9 (28-Dec-2013)
Étiquette de système de fichiers=
Type de système d'exploitation : Linux
Taille de bloc=4096 (log=2)
Taille de fragment=4096 (log=2)
« Stride » = 0 blocs, « Stripe width » = 0 blocs
327680 i-noeuds, 1310720 blocs
65536 blocs (5.00%) réservés pour le super utilisateur
Premier bloc de données=0
Nombre maximum de blocs du système de fichiers=1342177280
40 groupes de blocs
32768 blocs par groupe, 32768 fragments par groupe
8192 i-noeuds par groupe
Superblocs de secours stockés sur les blocs :
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736
Allocation des tables de groupe : complété
Écriture des tables d'i-noeuds : complété
Création du journal (32768 blocs) : complété
Écriture des superblocs et de l'information de comptabilité du système de
fichiers : complété
[root@centos ~]# mkfs -t ext4 /dev/vg01/lv02
[root@centos ~]# mkfs -t ext4 /dev/vg01/lv03
Create mount points
[root@centos mnt]# mkdir -p /mnt/volume1 /mnt/volume2 /mnt/volume3
[root@centos mnt]# mount -t ext4 /dev/vg01/lv01 /mnt/volume1/
[root@centos mnt]# mount -t ext4 /dev/vg01/lv02 /mnt/volume2/
[root@centos mnt]# mount -t ext4 /dev/vg01/lv03 /mnt/volume3/
[root@centos mnt]# touch /mnt/volume1/foo
Add permanent mount point in /etc/fstab
vim /etc/fstab
/dev/vg01/lv01 /mnt/volume1 ext4 defaults 0 0
/dev/vg01/lv02 /mnt/volume2 ext4 defaults 0 0
/dev/vg01/lv03 /mnt/volume3 ext4 defaults 0 0
reboot
df -h
/dev/mapper/vg01-lv02 15G 41M 14G 1% /mnt/volume2
/dev/mapper/vg01-lv03 7,8G 36M 7,3G 1% /mnt/volume3
/dev/mapper/vg01-lv01 4,8G 20M 4,6G 1% /mnt/volume1
Copy a full hard drive
[root@centos]# dd if=/dev/vg01/lv01 of=/dev/vg01/lv02
10485760+0 enregistrements lus
10485760+0 enregistrements écrits
5368709120 octets (5,4 GB) copiés, 102,314 s, 52,5 MB/s
Dump / restore
ls /mnt/volume4
umount /mnt/volume4
dump -0f /tmp/vol4.dump /dev/vg01/lv04
mount -t ext4 /dev/vg01/lv04 /mnt/volume4
rm -rf /mnt/volume4/*
cd /mnt/volume4
restore -rf /tmp/vol4.dump
ls
change root password
When starting the machine, interrupt the countdown by pressing any key
With the cursor on the start line
Hit "e" to edit the entry
Position on the line <br> by "linux16"
Move to the end of the line and add: rd.break
Hit Ctrl x to start the system with the modified configuration
When the "switch_root: / #" prompt appears, issue the following commands:
switch_root: / # mount -oremount, rw / sysroot
switch_root: / # chroot / sysroot
Change the root password:
# echo newmdp | passwd - root -stdin
or # passwd root
Editing the / etc / shadow file in out of context SELinux requires a full reboot of the system at the next reboot. To do this, enter the following command: # touch /.autorelabel
Hit the "exit" command twice, once to exit the chroot and a second time to the system.
When restarting the machine, the new operational password.